Ceramic materials and use of hydrogen
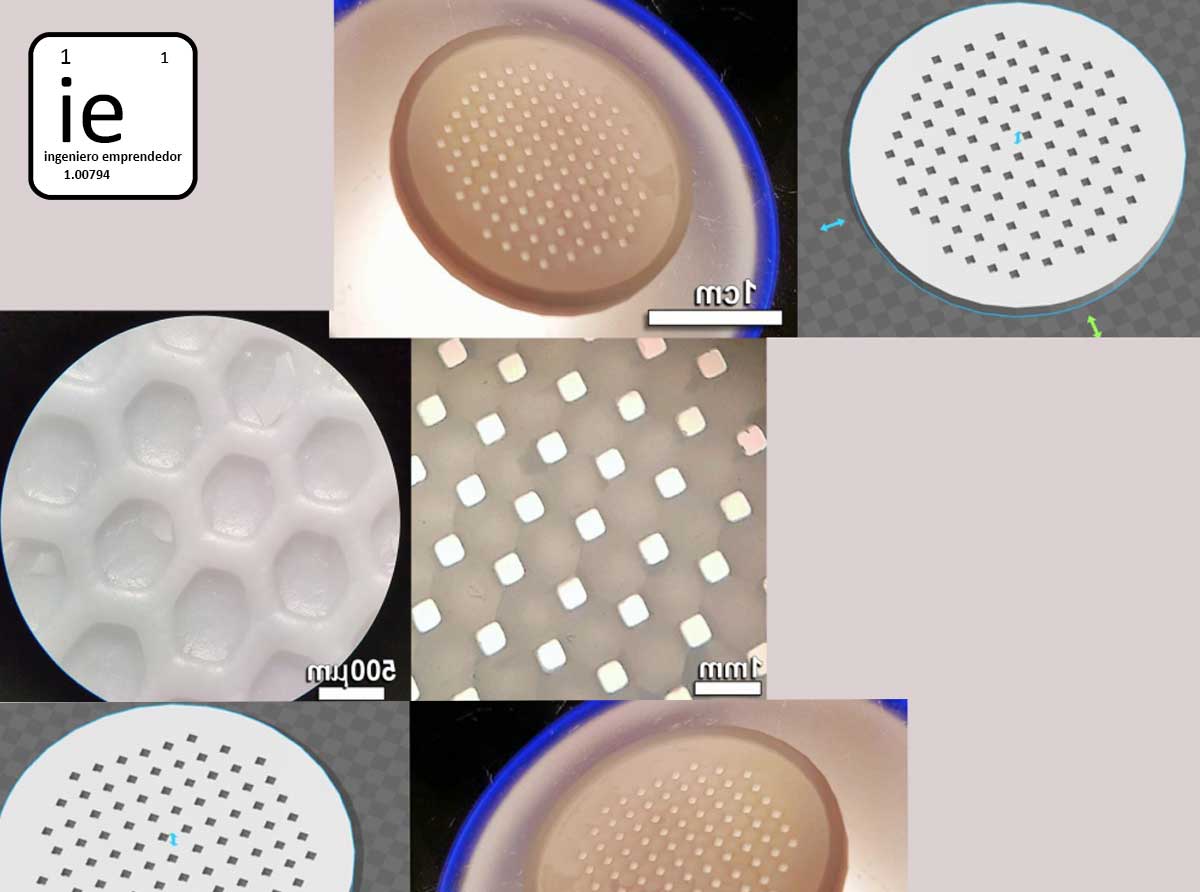
Advanced ceramic materials made using 3D printing:
In the last three decades there has been intense research into additive manufacturing technology (successive superimposition of micrometric layers of any material to make a particular structure) to produce three-dimensional objects without using special tools or molds. However, this technology has been restricted to polymers and metal parts and, until now, only a few functional ceramic materials have been available, preventing the use of this technology in the ceramic industry. A research group at the University of La Laguna has been able to manufacture advanced ceramic materials through the use of 3D printing.
Some impressions and comments:
“There are studies that indicate that the production of advanced ceramic materials using additive manufacturing techniques has the potential to generate an economic impact of between 230 and 500 million dollars until 2025,” says Juan Carlos Ruiz Morales, leader of the Nano group and Microengineering of Materials of the ULL.
The researcher explains that 3D printing is a low-cost additive manufacturing technology that “represents a new paradigm in the manufacture of energy systems. However, the manufacture of complex ceramic structures remains almost unexplored within this field, “he adds. “3D printing by means of ‘inkjet printing’ (3DP) or stereolithography (SLA) are particularly suitable methods that allow a wide variety of materials to be used in powder form or together use photosensitive resins which are selectively cured to produce a dense ceramic 3D material, With high resolution and fully functional, “continues the researcher.
The doctoral student Lorena Hernández Afonso, also of the group of Nano and Microengineering of Materials, has been in charge of designing, optimizing and printing in 3D advanced ceramic materials, based on zirconia and stable at temperatures above 1,400 ° C.
SLA printing has been used to manufacture new 3D structures, which do not exist today, and will allow, among other objectives, to manufacture fuel cells more efficient that can not be achieved by conventional methods. “In addition, these conventional methods usually produce up to 80% more waste products, so 3D printing promotes a circular economy that encourages the recycling of manufacturing products,” says Ruiz Morales.
Its objectives are related to hydrogen:
These objectives are focused on trying to change the current energy model based on the combustion of hydrocarbons, thus seeking new cleaner and more efficient energy production routes, such as the use of hydrogen in fuel cells producing zero pollutants, or using This same hydrogen and new 3D structures of photocatalyzed not only to catch the CO2 but to turn it into a fuel and therefore give economic value to what is usually considered only a pollutant.

























Excellent post. Keep writing such kind of information on your blog.
Im really impressed by your site.
Hi there, You have done an incredible job. I’ll definitely digg it and for my part recommend to my friends.
It’s an remarkable piece of writing in favor of all the
internet viewers; they will get benefit from it I am sure.
What a excellent article I’ve only finished.